The Hertzian contact theory calculates the contact area and pressures between to surfaces. As two objects come into contact, under loading, the solids deform and a contact area is formed as shown:
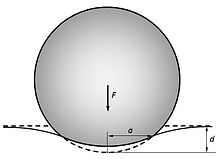
Contact area of a solid under an applied force [1].
The contact theory allows for the estimation of the resulting contact area, pressure, and stress in the solid. The assumptions behind the theory are that the solid is elastic, surfaces friction-less, and the strains are small. These assumptions allow us to imply that the contact area is much smaller than the radius of the contacting solid. For a sphere contacting a plane, the area can be approximated as described in Contact Area of Particle-Plane Impact.
Depending on the shape of the two contacting bodies, the approximation of the contact area can differ. In general form, the normal load applied over the contacting bodies is the force, F, applied over the area. With the loads and area established, the stresses on the bodies can be calculated along the major coordinate axes as principle stresses. The dominant stress will occur along the axis the load is applied and using the Mohr’s circle, the maximum shear stress can be determined.